Fuse Boards
 A fuse board (also known as a consumer unit or electrical fuse box) is designed to distribute electricity from your mains supply to the individual circuits in your home.
A fuse board (also known as a consumer unit or electrical fuse box) is designed to distribute electricity from your mains supply to the individual circuits in your home.
As well as being the control centre for your power supply, it has an important safety function as each circuit is monitored and the system will trip if any overloads are detected. Typically, a distribution board is a slightly more complex version of a fuse board. Homes can have either type although a distribution board is usually found in bigger buildings.
It's important that you know where your fuse box is located and that you familiarise yourself with how it works so that you can turn the power off in an emergency.
Finding your fuse box
Usually, fuse boxes are found in kitchens, utiliy rooms, porches or in the under-the-stairs cupboard. You should have easy access to it and it is sensible to ensure that the area around it is free from clutter. You want to be able to find it easily if your power goes out.
If your fuse box is located higher up on a wall you need to remember to have a step ladder handy so you can reach it.
What it looks like
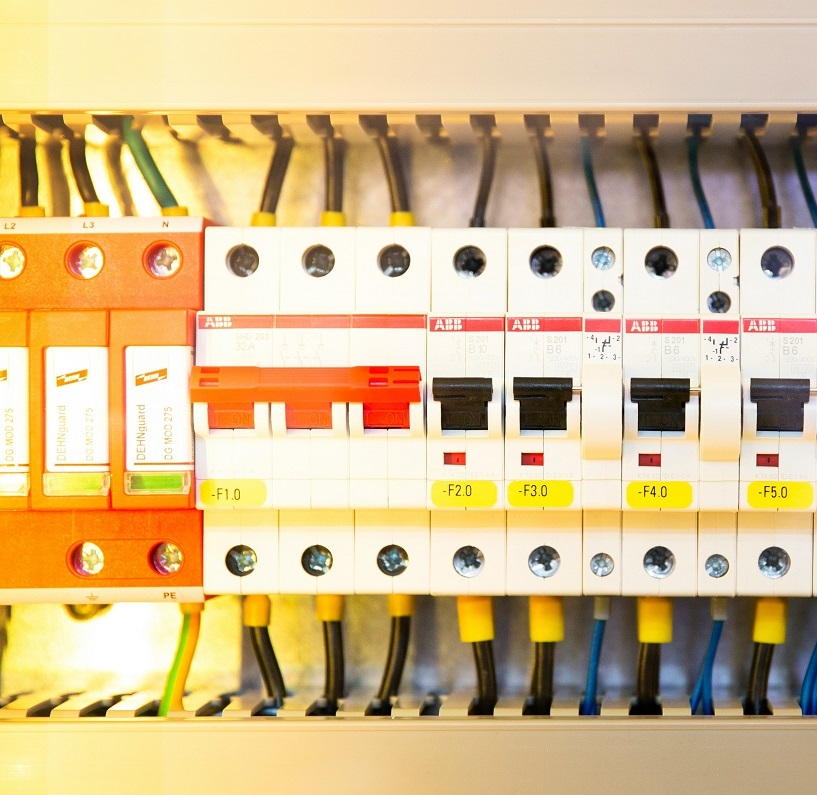
A domestic fuse box contains 3 key sets of switches, each of which serves a different purpose.
Mains switch
The mains switch in your fuse box is designed to turn off the electricity to your property. It's usually much bigger than the others and in the UK, bright red.
Some properties have more than one switch because there is more than one fuse board because of a specific need. For example if you have electric storage heaters, it's standard to have them on a separate fuse board.
Residual Current Devices (RCDs)
These are responsible for monitoring the electrical supply to a circuit and switching it off when a dangerous fault is detected. They are a vital part of the safety system of a fuse board as they cut off the electricity when there is a fault with wiring, a fault with a household appliance or if a person touches a live cable.
You should test these every three months to ensure that they are working properly. Next to the RCD switches is a "test" button. Press it and it should through up a fault to trip the switch. If they are working, the switch should move into the down position, switching the circuit off.
If the test does not trip the switch, there could be a fault on the fuse board. Contact us here for advice.
Unless you are a qualified electrician, do not attempt to fix your board yourself. Electricity is dangerous and you could put yourself, those living in your home and your property at risk.
Circuit breakers
Circuit breakers are the final type of switch you will find inside a domestic fuse board. These switch a circuit off if they detect a fault, working in a similar way to a traditional wire fuse.
Old fuse boxes
If your fuse box has a wooden back, features cast iron switches or a mixture of different fuses, it probably dates back to before the 1960s. You must get your fuse box upgraded to a more modern version to keep those living in your household safe.
My fuse box keeps tripping
If the switches in your fuse box keep tripping, it’s a sign that something is wrong with the wiring in your home or you’ve got a dodgy appliance. Try to avoid continuously resetting your circuit breakers, as this will cause damage to the wiring.
If you can’t put your finger on it or you are dealing with faulty electrics, please get in touch with us here.